Azure Portal: 7 Powerful Features You Must Master Today
Welcome to the ultimate guide on the Azure Portal—your central hub for managing Microsoft’s cloud ecosystem. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned cloud pro, mastering this powerful interface can transform how you deploy, monitor, and scale resources with ease and precision.
What Is the Azure Portal and Why It Matters

The Azure Portal is Microsoft’s web-based interface for managing cloud services across the Azure platform. It provides a unified dashboard where users can create, configure, monitor, and manage all Azure resources—from virtual machines to AI services—using an intuitive graphical user interface (GUI).
Definition and Core Purpose
The Azure Portal, officially known as the Azure management portal, is a secure, browser-accessible platform that acts as the control center for Azure cloud services. It allows users to interact with Azure resources without needing deep command-line expertise, making cloud management accessible to a broader audience.
- It serves as a centralized management console for all Azure services.
- Users can deploy, scale, and monitor resources in real time.
- It supports role-based access control (RBAC), enabling secure team collaboration.
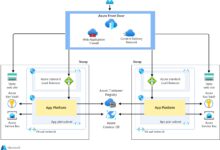
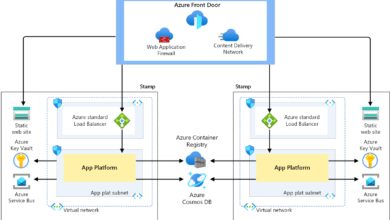
How It Fits Into the Microsoft Cloud Ecosystem
The Azure Portal is not a standalone tool—it’s deeply integrated with other Microsoft services such as Azure Active Directory, Microsoft 365, and Dynamics 365. This integration allows organizations to manage identity, compliance, and productivity tools from a single pane of glass.
For example, administrators can use the Azure Portal to configure conditional access policies through Azure AD, ensuring that only compliant devices can access corporate resources. This level of integration enhances security and simplifies governance across hybrid environments.
“The Azure Portal is the front door to the cloud for millions of IT professionals worldwide.” — Microsoft Cloud Documentation
Navigating the Azure Portal Interface Like a Pro
One of the biggest advantages of the Azure Portal is its user-friendly interface. However, its depth and breadth can be overwhelming for new users. Understanding the layout and navigation elements is key to unlocking its full potential.
Dashboard and Home Screen Overview
When you first log in to the Azure Portal, you’re greeted with a customizable dashboard. This dashboard can be personalized with tiles that represent your most-used services, resource health, cost analysis, and more.
- You can pin resources like VMs, storage accounts, or databases for quick access.
- The default view includes widgets for cost management, security alerts, and service health.
- Multiple dashboards can be created for different teams or projects.
Main Menu and Service Navigation
The left-hand navigation pane is the backbone of the Azure Portal. It provides access to all Azure services, grouped into logical categories such as Compute, Networking, Storage, and Security.
Key sections include:
- All Services: A comprehensive list of every available Azure resource.
- Resource Groups: Logical containers that help organize and manage related resources.
- Monitor: Tools for tracking performance, logs, and alerts.
- Cost Management + Billing: Critical for tracking spending and optimizing cloud costs.
Using filters and search functionality, users can quickly locate specific services—such as “Virtual Machines” or “Azure Functions”—without scrolling through long menus.
Managing Resources Through the Azure Portal
At the heart of the Azure Portal is resource management. Whether you’re deploying a single virtual machine or orchestrating a multi-tier application, the portal provides the tools to do it efficiently.
Creating and Deploying Virtual Machines
One of the most common tasks in the Azure Portal is creating virtual machines (VMs). The process is streamlined with guided wizards that walk users through configuration options.
- Select the operating system (Windows, Linux, or specialized images).
- Choose VM size based on CPU, memory, and performance needs.
- Configure networking, storage, and security settings in one workflow.
You can also deploy VMs from templates or use Azure Marketplace images for pre-configured solutions like WordPress or SQL Server.
Working with Resource Groups and Tags
Resource groups are essential for organizing and managing Azure assets. They allow you to group related resources—such as a web app, database, and storage account—so they can be managed, monitored, and deleted together.
Tags add another layer of organization. You can apply metadata like “Environment: Production” or “Department: Finance” to resources, enabling better cost tracking and policy enforcement.
- Tags are key-value pairs that can be used in automation and reporting.
- They integrate with Azure Policy to enforce compliance rules.
- Cost analysis tools can break down spending by tag, helping finance teams understand cloud usage.
Monitoring and Security in the Azure Portal
Visibility and security are critical in any cloud environment. The Azure Portal offers robust tools to monitor system performance and protect your infrastructure from threats.
Using Azure Monitor and Logs
Azure Monitor is a comprehensive observability platform integrated directly into the Azure Portal. It collects telemetry from your applications and infrastructure, providing insights into performance and availability.
- Collect metrics, logs, and traces from VMs, apps, and networks.
- Create custom dashboards to visualize system health.
- Set up alerts based on thresholds (e.g., CPU usage > 80%).
Log Analytics, a component of Azure Monitor, allows you to run Kusto Query Language (KQL) queries to analyze log data and detect anomalies.
Security Center and Compliance Tools
Azure Security Center (now part of Microsoft Defender for Cloud) provides unified security management and advanced threat protection across hybrid cloud workloads.
- It continuously assesses your environment for vulnerabilities.
- Recommends security improvements like enabling disk encryption or configuring firewalls.
- Integrates with third-party tools and SIEMs via connectors.
Compliance dashboards show how your resources align with standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001, making audits easier and reducing risk.
Automation and DevOps Integration via Azure Portal
The Azure Portal isn’t just for manual operations—it’s a gateway to automation and DevOps practices that accelerate software delivery and improve reliability.
Using Azure Automation and Runbooks
Azure Automation allows you to automate repetitive tasks using runbooks—scripts written in PowerShell or Python that execute within Azure.
- Automate VM start/stop schedules to reduce costs.
- Synchronize user accounts between on-premises and cloud directories.
- Perform routine maintenance like patching and backups.
Runbooks can be triggered manually, on a schedule, or by events using Azure Logic Apps or Event Grid.
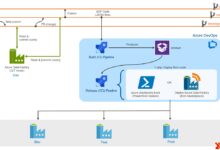
Integration with Azure DevOps and CI/CD Pipelines
The Azure Portal integrates seamlessly with Azure DevOps to support continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD).
- Deploy applications directly from repositories like GitHub or Azure Repos.
- Use deployment centers in App Services to configure pipelines with minimal effort.
- Monitor build and release statuses directly from the portal.
This integration enables development teams to ship code faster while maintaining control over environments and rollback procedures.
Cost Management and Optimization in the Azure Portal
One of the biggest challenges in cloud computing is controlling costs. The Azure Portal provides powerful tools to track, analyze, and optimize your cloud spending.
Understanding the Cost Management Dashboard
The Cost Management + Billing section of the Azure Portal gives you real-time visibility into your spending. You can view costs by service, region, resource group, or tag.
- See daily and monthly trends with interactive charts.
- Compare actual spend against budgets.
- Download detailed reports for financial analysis.
Budgets can be set at the subscription or resource group level, with alerts sent via email or webhook when thresholds are exceeded.
Right-Sizing Resources and Using Reserved Instances
To optimize costs, Azure recommends right-sizing—matching resource capacity to actual workload demands.
- Use Azure Advisor to get recommendations on downsizing underutilized VMs.
- Purchase Reserved Virtual Machine Instances for up to 72% savings on long-running workloads.
- Leverage Spot VMs for fault-tolerant, batch-processing jobs at a fraction of the cost.
These strategies, when applied through the Azure Portal, can lead to significant cost reductions without sacrificing performance.
Advanced Tips and Hidden Features of the Azure Portal
Beyond the basics, the Azure Portal offers several advanced features that power users leverage to boost productivity and streamline operations.
Customizing Dashboards for Teams
Dashboards in the Azure Portal aren’t just personal—they can be shared across teams. This is especially useful for operations, security, or finance teams that need a consistent view of key metrics.
- Create role-specific dashboards (e.g., a security ops dashboard).
- Share dashboards via URL or integrate them into internal wikis.
- Use Azure Portal’s export feature to back up dashboard configurations.
Custom tiles can display live data from Azure Monitor, Logic Apps, or even external APIs using embedded web content.
Leveraging the Cloud Shell and CLI Integration
The Azure Portal includes an embedded Azure Cloud Shell, a browser-based command-line environment that supports both Bash and PowerShell.
- No installation required—runs directly in the browser.
- Pre-authenticated with your Azure session, so no need to log in again.
- Persistent storage via an Azure file share for saving scripts and configurations.
This allows users to combine GUI navigation with CLI commands, making complex tasks faster and more repeatable.
Common Challenges and Best Practices When Using Azure Portal
While the Azure Portal is powerful, it comes with challenges—especially in large or complex environments. Knowing best practices can help avoid common pitfalls.
Avoiding Permission and Access Issues
One of the most frequent issues in Azure is misconfigured permissions. Without proper role-based access control (RBAC), users may have too much or too little access.
- Follow the principle of least privilege—grant only the permissions needed.
- Use built-in roles like Reader, Contributor, and Owner appropriately.
- Create custom roles for specialized access requirements.
Regularly audit access using Azure AD’s access reviews to ensure compliance.
Ensuring Consistency Across Environments
Inconsistent configurations between development, testing, and production environments can lead to outages and security gaps.
- Use Azure Blueprints to define and enforce standardized environments.
- Deploy infrastructure as code (IaC) using ARM templates or Bicep files via the portal.
- Enable Azure Policy to automatically audit and remediate non-compliant resources.
These practices ensure that environments are predictable, secure, and easier to manage at scale.
What is the Azure Portal?
The Azure Portal is a web-based console provided by Microsoft for managing Azure cloud services. It allows users to deploy, configure, monitor, and manage resources like virtual machines, databases, and networks through an intuitive interface.
How do I access the Azure Portal?
You can access the Azure Portal by visiting portal.azure.com and signing in with your Microsoft or Azure Active Directory account. Multi-factor authentication is recommended for security.
Is the Azure Portal free to use?
Yes, the Azure Portal itself is free to access. However, the resources you create and manage within it (like VMs, storage, and bandwidth) incur costs based on usage. You can use the Azure Free Account to get started with limited free services.
Can I automate tasks in the Azure Portal?
Absolutely. The Azure Portal supports automation through tools like Azure Automation, Logic Apps, and integration with Azure DevOps. You can also use the embedded Cloud Shell to run PowerShell or Bash scripts for automated deployments and management.
How does the Azure Portal help with cost management?
The Azure Portal includes a comprehensive Cost Management + Billing dashboard that lets you track spending, set budgets, analyze costs by tags or resource groups, and receive alerts when usage exceeds thresholds. It also provides recommendations for cost optimization.
Mastering the Azure Portal is essential for anyone working with Microsoft’s cloud platform. From deploying virtual machines to securing environments and optimizing costs, the portal offers a powerful, unified interface that brings the full potential of Azure within reach. By leveraging its features—from dashboards and monitoring to automation and cost controls—you can streamline operations, enhance security, and drive efficiency across your cloud infrastructure. Whether you’re a developer, administrator, or decision-maker, investing time in learning the Azure Portal pays dividends in productivity and control.
Further Reading: