Azure Standard: 7 Powerful Insights You Must Know in 2024
Cloud computing has reshaped how businesses operate, and at the heart of this revolution is Microsoft Azure. But what exactly is the Azure standard, and why does it matter for your organization’s digital future? Let’s dive in.
Understanding the Azure Standard: A Foundational Overview

The term azure standard doesn’t refer to a single product but rather a set of benchmarks, service tiers, and best practices that define performance, availability, and cost-efficiency across Microsoft Azure’s vast cloud ecosystem. These standards help organizations make informed decisions when selecting virtual machines, storage options, networking configurations, and compliance frameworks.
What Does ‘Azure Standard’ Actually Mean?
In Microsoft Azure terminology, ‘Standard’ is a service tier designation used across multiple services—most notably Virtual Machines (VMs), Storage, and Load Balancers. It sits above the ‘Basic’ tier and below specialized tiers like ‘Premium’ or ‘Dedicated’. The azure standard tier offers a balanced mix of performance, scalability, and cost, making it ideal for production workloads that require high availability and enterprise-grade features.
- The ‘Standard’ tier supports SLA-backed uptime (typically 99.9%)
- It enables auto-scaling, load balancing, and zone redundancy
- It’s commonly used for web servers, application backends, and enterprise databases
How Azure Standard Compares to Other Tiers
Understanding the differences between service tiers is crucial. While the ‘Basic’ tier is designed for dev/test environments with no SLA guarantees, the azure standard tier is built for production use. For example, Azure Virtual Machines in the Standard tier support availability sets, scale sets, and integration with Azure Monitor—features absent in Basic.
“The Standard tier in Azure strikes the perfect balance between cost and capability for most enterprise applications.” — Microsoft Azure Architecture Center
Azure Standard Virtual Machines: Powering Enterprise Workloads
One of the most widely used implementations of the azure standard concept is within Azure Virtual Machines. These VMs are designed to deliver consistent performance, high availability, and seamless integration with other Azure services.
Key Features of Azure Standard VMs
Azure Standard VMs come with a range of capabilities that make them suitable for mission-critical applications. These include:
- Availability Sets: Distribute VMs across fault and update domains to minimize downtime during maintenance or hardware failures.
- Scale Sets: Automatically scale the number of VM instances based on demand, ensuring optimal performance during traffic spikes.
- Managed Disks: Built-in redundancy and backup support, with options for Standard HDD, Standard SSD, and integration with Azure Backup.
These features are not available in the Basic tier, reinforcing the value of the azure standard for production environments.
Use Cases for Standard VMs
Organizations leverage Azure Standard VMs in various scenarios:
- Web Hosting: Running scalable web applications using IIS, Apache, or Nginx with auto-scaling and load balancing.
- Enterprise Applications: Hosting ERP, CRM, or legacy systems that require stable performance and integration with on-premises networks via Azure ExpressRoute.
- DevOps Environments: Creating consistent, reproducible environments for CI/CD pipelines using Azure DevOps and GitHub Actions.
For more details, visit Microsoft’s official Azure Virtual Machines documentation.
Azure Standard Storage: Reliability Meets Affordability
Storage is a cornerstone of any cloud infrastructure, and Azure Standard Storage plays a pivotal role in delivering durable, cost-effective data solutions. When people refer to the azure standard in storage, they’re typically talking about Standard HDD and Standard SSD options.
Types of Azure Standard Storage
Azure offers several storage classes under the Standard tier:
- Standard HDD: Cost-efficient storage for infrequently accessed data, such as backups, logs, or archival content.
- Standard SSD: Balanced performance for moderate I/O workloads like web servers, small databases, and development environments.
- Standard Blob Storage: Designed for unstructured data like images, videos, and documents, with support for lifecycle management and access tiers.
Each of these options adheres to the azure standard of 99.9% availability and geo-redundant storage (GRS) options for disaster recovery.
Performance and Cost Considerations
While Premium SSDs offer higher IOPS and lower latency, the azure standard storage options provide a more budget-friendly alternative without sacrificing reliability. For example:
- Standard HDD: ~3,000 IOPS and 60 MiB/s throughput per disk
- Standard SSD: ~2,000 IOPS and 120 MiB/s throughput per disk
These specs are sufficient for many enterprise applications, especially when combined with Azure’s auto-tiering and caching technologies. Learn more at Azure Storage Overview.
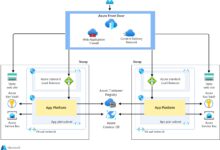
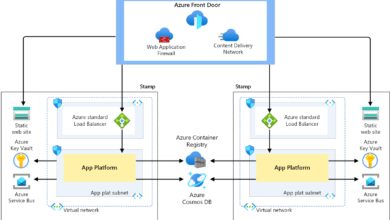
Networking and Load Balancing: The Azure Standard Tier Advantage
Networking is another domain where the azure standard tier shines. Azure Standard Load Balancer and Standard Public IP addresses offer advanced traffic distribution and high availability features essential for modern applications.
Azure Standard Load Balancer Capabilities
The Standard Load Balancer is designed for large-scale, high-availability applications. Key features include:
- Zone-redundant frontend: Distributes traffic across Availability Zones for resilience against zone failures.
- Outbound rules: Simplifies NAT configuration for outbound internet access from VMs.
- Integration with Network Security Groups (NSGs): Enables fine-grained traffic filtering and security policies.
Unlike the Basic Load Balancer, the Standard version supports backend pools with VMs from different availability sets and scales seamlessly with large deployments.
Standard Public IP and DNS Integration
Azure Standard Public IPs are required when using Standard Load Balancer. They offer:
- SLA-backed availability (99.99%)
- Zone redundancy for high-availability architectures
- Support for DNS name labels and integration with Azure DNS
These features make the azure standard networking stack ideal for global applications requiring low latency and high uptime. Explore more at Azure Load Balancer Documentation.
Security and Compliance: Azure Standard’s Role in Governance
Security is non-negotiable in the cloud, and the azure standard includes robust compliance and governance frameworks. Microsoft Azure adheres to over 100 compliance certifications, including ISO 27001, HIPAA, GDPR, and FedRAMP.
Standard Security Features Across Services
Even in the Standard tier, Azure provides enterprise-grade security:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Granular permissions management across subscriptions and resources.
- Network Security Groups (NSGs): Firewall-like rules to control inbound and outbound traffic.
- Azure Monitor and Log Analytics: Real-time monitoring and alerting for suspicious activities.
These tools are available across Standard-tier services, ensuring that security doesn’t come at a premium price.
Compliance Standards and Auditing
The azure standard also refers to Microsoft’s commitment to regulatory compliance. Azure Policy allows organizations to enforce governance rules at scale, such as:
- Enforcing encryption on all Standard Storage accounts
- Requiring VMs to be part of an availability set
- Automatically tagging resources for cost tracking
This proactive governance model helps businesses meet audit requirements without manual oversight. Learn about compliance at Microsoft Compliance Documentation.
Cost Management and Pricing Models for Azure Standard
One of the biggest advantages of the azure standard is its predictable and scalable pricing. Unlike on-premises infrastructure, Azure allows you to pay only for what you use, with multiple options to optimize costs.
Understanding Azure Standard Pricing
Pricing for Standard-tier services varies by region and usage. For example:
- Standard VMs: Billed per second (after the first minute) for compute, with separate charges for storage and networking.
- Standard Storage: Charged based on capacity, transactions, and data transfer.
- Standard Load Balancer: Free for inbound rules, with charges for outbound rules and data processing.
Microsoft provides a pricing calculator to estimate costs based on your workload.
Cost Optimization Strategies
To get the most value from the azure standard, consider these strategies:
- Reserved Instances: Commit to 1- or 3-year terms for VMs to save up to 72% compared to pay-as-you-go.
- Spot VMs: Use unused capacity for non-critical workloads at up to 90% discount.
- Auto-shutdown: Schedule VMs to turn off during non-business hours.
- Right-sizing: Regularly review VM performance and downsize underutilized instances.
These practices ensure that the azure standard remains both powerful and cost-effective.
Migration and Implementation: Adopting Azure Standard Best Practices
Moving to the azure standard requires careful planning. Whether you’re migrating from on-premises, another cloud provider, or upgrading from Basic tiers, following best practices ensures a smooth transition.
Assessment and Planning Tools
Microsoft offers several tools to assess your current environment:
- Azure Migrate: Discovers on-premises servers, assesses compatibility, and estimates costs for migration.
- Site Recovery: Enables seamless failover and failback for disaster recovery scenarios.
- Cost Management + Billing: Tracks spending and identifies optimization opportunities post-migration.
These tools help organizations adopt the azure standard with minimal risk.
Implementation Roadmap
A successful implementation follows these steps:
- Discovery: Inventory existing workloads and dependencies.
- Assessment: Use Azure Migrate to evaluate suitability for Standard-tier services.
- Design: Architect solutions with availability sets, load balancers, and secure networking.
- Migrate: Use Azure Site Recovery or Azure Database Migration Service.
- Optimize: Apply cost controls, monitoring, and auto-scaling policies.
For guidance, refer to the Azure Architecture Center.
Future Trends: How Azure Standard is Evolving
The azure standard is not static—it evolves with technology. Microsoft continuously enhances Standard-tier services with new features, improved performance, and deeper integration with AI and hybrid cloud solutions.
Integration with AI and Machine Learning
Azure Standard VMs now support AI workloads through integration with Azure Machine Learning and Cognitive Services. For example, Standard NV-series VMs provide GPU acceleration for moderate AI training tasks, making advanced analytics accessible without premium pricing.
Hybrid Cloud and Azure Arc
Azure Arc extends the azure standard to on-premises and multi-cloud environments. With Arc, you can manage servers, Kubernetes clusters, and data services using the same tools and policies as native Azure resources.
- Apply Azure RBAC and Policy to non-Azure machines
- Monitor hybrid environments with Azure Monitor
- Deploy Azure services on-premises using Azure Stack HCI
This convergence ensures that the azure standard is not limited to the public cloud but represents a unified operational model across all infrastructures.
Sustainability and Green Computing
Microsoft is committed to sustainability, and the azure standard includes energy-efficient data centers powered by renewable energy. Azure’s carbon-aware scheduling and region selection tools help organizations reduce their environmental impact while maintaining performance.
Learn more about Microsoft’s sustainability goals at Microsoft Sustainability.
What is the Azure Standard tier?
The Azure Standard tier refers to a service level in Microsoft Azure that offers a balance of performance, availability, and cost. It is designed for production workloads and includes features like SLA-backed uptime, auto-scaling, and enterprise-grade security.
How does Azure Standard differ from Basic and Premium tiers?
The Basic tier is for non-production use with no SLA, while the Standard tier supports production workloads with 99.9% uptime SLA. Premium offers higher performance (e.g., faster SSDs, higher IOPS) for latency-sensitive applications.
Is Azure Standard suitable for enterprise applications?
Yes, Azure Standard is widely used for enterprise applications due to its reliability, scalability, and compliance features. It supports high-availability architectures, hybrid connectivity, and advanced monitoring.
Can I migrate from Basic to Azure Standard?
Yes, you can upgrade from Basic to Standard tiers for services like VMs and Load Balancers. However, this often requires redeployment or configuration changes, so planning with Azure Migrate is recommended.
How can I optimize costs with Azure Standard?
You can optimize costs by using Reserved Instances, Spot VMs, auto-shutdown policies, and right-sizing resources. Azure Cost Management tools help monitor and control spending.
Understanding the azure standard is essential for any organization leveraging Microsoft Azure. From virtual machines and storage to networking and compliance, the Standard tier offers a robust, scalable, and secure foundation for modern cloud applications. By adopting best practices in cost management, security, and hybrid integration, businesses can fully harness the power of Azure while maintaining control over performance and expenses. As cloud technology evolves, the azure standard continues to set the benchmark for reliability, innovation, and enterprise readiness.
Further Reading: